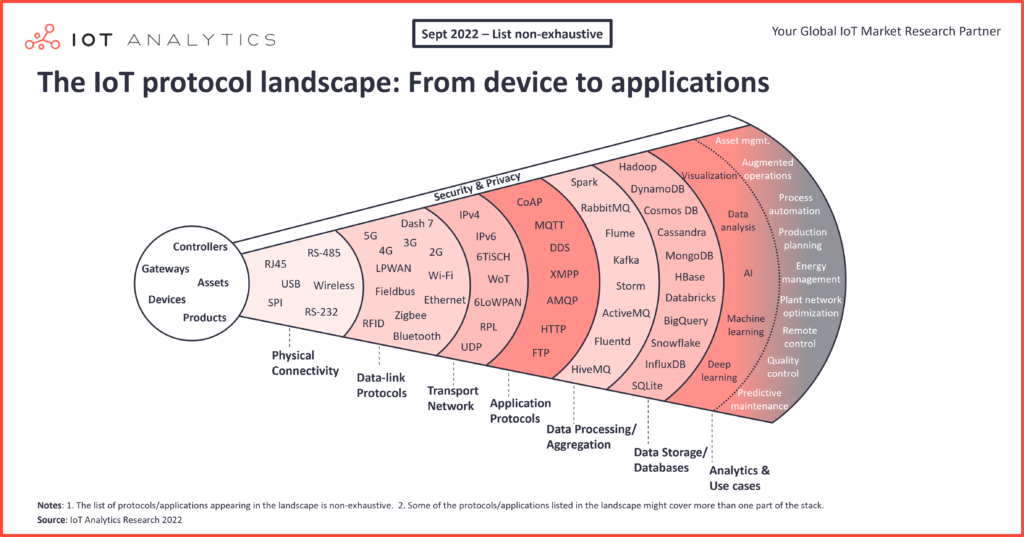
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized how we interact with technology, businesses, and our everyday lives. The seamless connectivity of devices, systems, and services has transformed industries and paved the way for a new wave of innovation. At the heart of this transformation are the various communication protocols that enable devices to share data and interact. Understanding the market share of these protocols is crucial for stakeholders, manufacturers, and developers to choose the right tools for their applications.
Understanding IoT Protocols
Before delving into the market share, it’s essential to understand what IoT protocols are. These communication standards define how devices communicate with one another over the internet. They govern data formats, transmission methods, and the rules for communication, ensuring that devices can interact smoothly within interconnected systems.
Several protocols have emerged over the years, each tailored for specific use cases, bandwidth requirements, power consumption levels, and network architecture. Some of the most prominent IoT protocols include MQTT, CoAP, HTTP/HTTPS, AMQP, Zigbee, LoRaWAN, and Bluetooth.
A Breakdown of Major IoT Protocols
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport):
MQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol designed for low-bandwidth and high-latency networks. It is widely popular because of its efficient use of bandwidth and power, making it ideal for devices with limited resources. In the realm of IoT, MQTT has garnered significant traction, particularly in industries like smart homes, manufacturing, and healthcare. - CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol):
Designed specifically for use with constrained devices and networks, CoAP allows devices in the IoT ecosystem to communicate in a simple, efficient manner. It is often used in machine-to-machine (M2M) applications and has seen considerable adoption in smart city initiatives and building automation. - HTTP/HTTPS:
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol is the foundation of communication on the web. Although not optimized for IoT, HTTP/HTTPS remains vital due to its ubiquity. Many IoT applications still rely on HTTP for communication, particularly those requiring interaction with web services. - AMQP (Advanced Message Queuing Protocol):
AMQP is used for message-oriented middleware and facilitates secure, interoperable, and reliable messaging. It is predominantly utilized in industries that require robust transaction handling, including finance and logistics. - Zigbee:
A low-power, low-data-rate wireless network protocol, Zigbee is widely used in home automation, industrial control, and smart energy applications. Its mesh network capabilities allow devices to communicate over long distances, making it a reliable choice for home security systems and smart appliances. - LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network):
LoRaWAN is designed for long-range, low-power communications, making it an ideal choice for applications that require wide coverage, such as agricultural monitoring and urban infrastructure management. The protocol’s ability to cover several kilometers and its low energy consumption have driven its adoption in rural and remote areas. - Bluetooth:
Bluetooth technology has grown from simple connectivity for devices like headsets and smartphones to supporting complex IoT applications. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is particularly suitable for battery-operated devices and health monitoring applications.
According to various industry reports and market analyses as of 2023, the market share of these protocols reflects a diversified landscape influenced by several factors, including industry needs, geographic trends, and technological advancements. Here’s how these protocols stack up in terms of market adoption:
- MQTT: Commanding a strong share of about 28% of the IoT protocol market, MQTT’s popularity stems from its efficiency and suitability for applications demanding real-time data exchange, such as smart home technologies and industrial frameworks.
- HTTP/HTTPS: Holding a steady market share of approximately 25%, HTTP remains prevalent due to its simplicity and wide acceptance across the web, even in IoT applications where traditional web services are involved.
- Zigbee: With around 18% of the market, Zigbee thrives in niche applications, particularly in home automation and smart energy solutions, where its mesh networking capabilities are beneficial.
- LoRaWAN: Gaining momentum, LoRaWAN has captured about 15% of the market share and is on the rise, particularly in agriculture and environmental monitoring due to its long-range capabilities.
- CoAP: Representing around 10% of the market, CoAP is increasingly adopted for M2M communications and among service providers focusing on efficient resource usage.
- Bluetooth (including BLE): Accounting for around 4% of the IoT protocol market, while it is much less than others, its ease of use in consumer electronics keeps it relevant in private and personal applications.
- AMQP: Although not as widely adopted, AMQP holds about 3% of the market, primarily in sectors that require high transaction security.
Trends Influencing IoT Protocol Adoption
Several trends are influencing the shifting landscape of IoT protocols, including:
- Increased Focus on Security: As IoT devices proliferate, so do security concerns. Protocols ensuring robust security measures for privacy and data integrity are witnessing increased attention.
- Interoperability: With a growing number of devices in the IoT ecosystem, interoperability remains a significant requirement. Protocols that facilitate seamless communication between diverse devices and platforms are becoming increasingly crucial.
- Low Power Consumption Needs: As battery-operated devices continue to rise, there’s a push for protocols designed for low power consumption, which increases the adoption of solutions like LoRaWAN and BLE.
- Scalability: Organizations are looking for scalable solutions that can accommodate multiple devices without compromising efficiency. Protocols that can ensure scalability will likely gain more traction.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things is an ever-evolving field, and understanding the market share of various IoT protocols is essential for stakeholders aiming to make informed decisions. As the landscape continues to shift with new technologies and changing demands, the choice of protocol will play a pivotal role in the success of IoT solutions. By staying informed on the current trends and market dynamics, businesses can harness the power of IoT effectively, driving innovation and efficiency in their operations.
In summary, MQTT continues to dominate the protocol market, but competition is fierce, with HTTP/HTTPS, Zigbee, and LoRaWAN making significant inroads. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each protocol will be key for developers and organizations as they navigate the future of IoT.